Table of Contents
- What is Cloud ERP
- How Cloud ERP Works
- Key Features of Cloud ERP Software
- Benefits of Cloud ERP
- Cloud ERP Concepts
- On-Premises ERP vs. Cloud ERP
- ERP vs. Cloud ERP
- Types of Cloud ERP Software
- Cloud ERP Challenges and Risks
- Mid-Market Companies Choose Cloud ERP
- Market Trends of Cloud ERP
- Top Cloud ERP Providers
- Conclusion
- FAQs of Cloud ERP Software
In today’s fast-paced business world, efficiency and agility can make the difference between growth and stagnation. That’s where Cloud ERP software steps in. From finance to supply chain, it unifies critical business functions into one system that’s accessible anytime, anywhere. But what exactly is cloud ERP, how does it differ from traditional ERP, and what trends are shaping its future?
This guide walks you through everything-from features and benefits to challenges, market trends, and leading providers in 2025.
What is Cloud ERP?
In simple terms, it is a modern evolution of the traditional ERP system. When people ask, ‘What is an ERP system?‘ the answer today often includes cloud-based ERP solutions that are scalable, flexible, and easier to deploy than legacy ERP software.
Cloud ERP, or Cloud Enterprise Resource Planning, is a software solution hosted on remote servers and delivered via the internet. Unlike traditional ERP that sits on local servers, cloud ERP uses cloud computing technology to centralize business data, making it accessible in real time from any device. Unlike older enterprise resource planning ERP models, cloud ERP software is designed to adapt quickly, offering scalable ERP solutions for businesses of all sizes.
Think of it as a digital nervous system for your company-finance, HR, inventory, sales, and customer management all run through one integrated platform. Instead of worrying about hardware, licenses, or updates, you simply pay a subscription and focus on running your business.
How Cloud ERP Works?
At its core, cloud ERP operates as a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model. Businesses log in via a secure browser or mobile app, while the ERP provider manages the infrastructure, security, and updates behind the scenes. In a short cloud ERP system, it functions as a SaaS ERP system, making it cost-effective and easier to manage compared to legacy ERP software.
Here’s how it works in practice:
- A sales order entered by your team instantly updates your inventory, finance, and logistics modules.
- Executives can pull real-time dashboards showing revenue trends without waiting for reports.
- Updates happen automatically, meaning you’re always running on the latest version.
This interconnected system ensures decisions are based on accurate, up-to-the-minute data.
Key Features of Cloud ERP Software
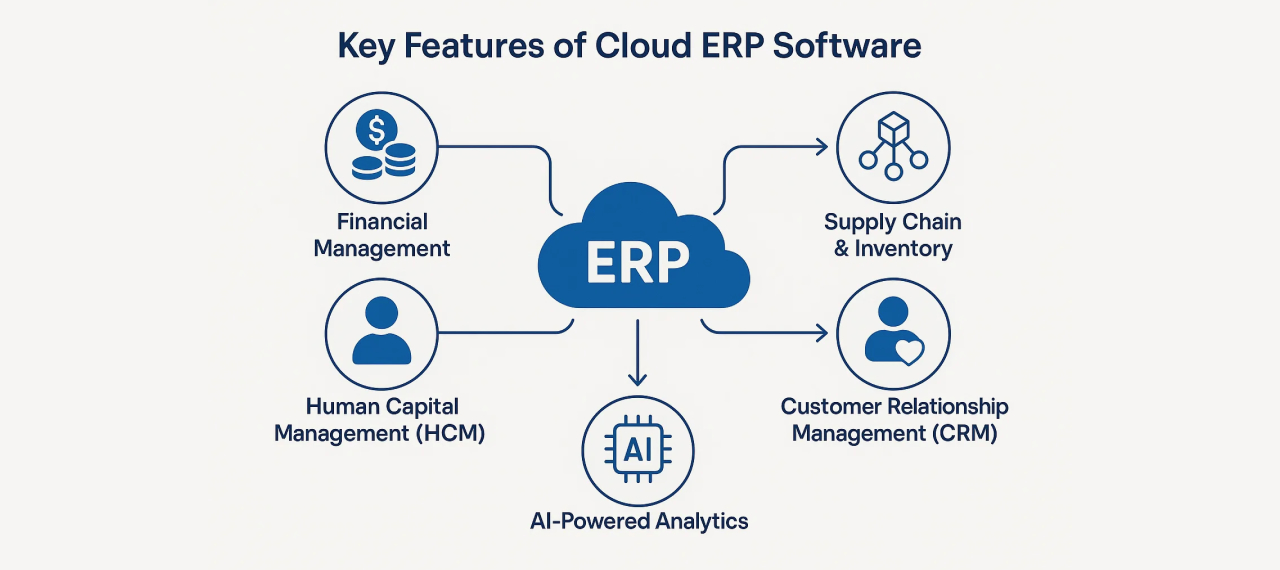
Many modern solutions also include ERP integration with CRM, ensuring that sales and customer service teams work seamlessly with finance and operations. Some of the standout features include:
1. Single Database
Cloud ERP systems are built on a centralized database, ensuring all business functions—from accounting to HR-are connected. This eliminates data silos, reduces duplication, and provides a “single source of truth” for the organization.
Benefit: Eliminates duplication, ensures accuracy, and provides holistic insights into business health.
Example: A retail company can track stock movement, sales, and revenue from one dashboard.
2. Real-Time Data
ERP software delivers instant access to data across departments. Real-time reporting enables managers to track performance, inventory, or financial health immediately, improving responsiveness and decision-making.
Benefit: Faster decisions, reduced delays, and proactive issue resolution.
Example: A logistics firm can see delivery status in real time, improving customer satisfaction.
3. Accounting
Core accounting features include general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, and bank reconciliation. Cloud ERP automates routine financial tasks, ensuring accuracy while reducing manual effort.
Benefit: Reduces manual errors, saves time, and ensures compliance with financial standards.
Example: Automates monthly balance sheets and reconciliations for finance teams.
4. Financial Management
Beyond accounting, ERP provides budgeting, forecasting, tax compliance, and expense tracking. This holistic view of financials helps in strategic planning and regulatory compliance.
Benefit: Helps leaders plan investments, optimize spending, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Example: A startup can predict funding requirements for the next quarter.
5. Order Processing
From order entry to fulfillment, ERP streamlines order management. Integration with inventory and logistics ensures faster order handling, fewer errors, and better customer satisfaction.
Benefit: Faster fulfillment, accurate inventory tracking, and better customer experience.
Example: eCommerce businesses can automate order confirmations, shipping, and invoicing.
6. Sales Management
ERP supports lead-to-cash processes by tracking opportunities, quotes, invoices, and after-sales service, ensuring smooth sales cycles and strong customer relationships.
Benefit: Helps sales teams close deals faster and track performance.
Example: A sales rep can generate invoices directly from the ERP after a deal closes.
7. CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
Integrated CRM allows businesses to manage customer data, interactions, and preferences. This feature helps boost retention, cross-selling, and overall customer satisfaction.
Benefit: Increases loyalty, supports targeted campaigns, and improves service.
Example: A SaaS company can send personalized renewal reminders.
8. Marketing
Some ERP systems embed marketing automation tools to manage campaigns, analyze customer behavior, and integrate with sales data, enabling more targeted and effective marketing.
Benefit: Aligns marketing with sales for higher conversions.
Example: ERP integrates with Mailchimp or HubSpot to manage campaigns inside the system.
9. Human Resource (HR)
HR modules include employee records, payroll, attendance, recruitment, and performance management. Cloud-based HR ensures smooth workforce management, even for remote teams.
Benefit: Centralizes workforce data, simplifies payroll, and boosts HR efficiency.
Example: Automates salary slips and employee onboarding processes.
10. Project Management
Enables teams to plan, assign resources, set budgets, and track project milestones. Integrated dashboards provide visibility into timelines and project profitability.
Benefit: Ensures projects stay on budget and on time.
Example: An IT services firm can track billable hours and project deadlines.
11. Manufacturing
ERP supports production planning, quality control, bill of materials (BOM), and shop floor management. This ensures efficient operations, reduced downtime, and optimized resource use.
Benefit: Increases output efficiency and reduces downtime.
Example: A factory can use ERP to plan raw material usage and reduce waste.
12. Supply Chain & Purchasing
Cloud ERP manages procurement, vendor relationships, and inventory levels. Automated workflows reduce costs, prevent stockouts, and optimize supply chain visibility.
Benefit: Optimizes inventory, cuts procurement delays, and reduces costs.
Example: Auto-reorder functionality for critical raw materials.
13. Business Process Controls
Standardized workflows and built-in checks reduce errors and fraud. For example, approvals for invoices or purchases ensure accountability across departments.
Benefit: Minimizes fraud, improves compliance, and ensures accountability.
Example: Expense approvals routed through department heads automatically.
14. Automation
Repetitive tasks like data entry, payroll, and reporting are automated. This reduces manual errors, saves time, and frees staff for more strategic work.
Benefit: Saves time, minimizes human error, and boosts efficiency.
Example: Monthly payroll is automatically processed and credited.
15. System Integration / Integration Capabilities
Cloud ERP integrates with CRMs, eCommerce platforms, POS systems, and third-party apps via APIs. This ensures seamless business operations without juggling multiple tools.
Benefit: Provides smooth data flow across systems.
Example: Shopify orders are automatically synced into ERP for inventory tracking.
16. Advanced Analytics & Reporting
Customizable dashboards and visual reports help analyze trends, KPIs, and forecasts. Cloud ERP often includes drill-down capabilities for deeper insights.
Benefit: Turns raw data into actionable insights.
Example: Sales forecasting dashboards to predict next quarter’s revenue.
17. Embedded AI
Modern ERP leverages artificial intelligence for demand forecasting, anomaly detection, and predictive maintenance-helping businesses stay ahead.
Benefit: Increases accuracy and efficiency through predictive insights.
Example: AI suggests stock replenishment levels based on buying patterns.
18. Data Security & Compliance
Cloud ERP providers ensure compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX. Data is encrypted, with role-based access to protect sensitive information.
Benefit: Safeguards sensitive data and meets regulatory standards.
Example: Automatically ensures financial reports meet SOX compliance.
19. Enhanced Cybersecurity
Beyond compliance, advanced security features like firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection protect against cyber threats.
Benefit: Defends against cyberattacks and data breaches.
Example: Unusual login attempts trigger alerts instantly.
20. Automatic Updates
Unlike on-premise systems, cloud ERP updates automatically, ensuring access to the latest features and security patches without disruption.
Benefit: Businesses always use the latest technology without extra IT costs.
Example: A new reporting module appears automatically after an update.
Unlike outdated systems, these features are designed for flexibility and real-time collaboration.
Benefits of Cloud ERP for Businesses
Cloud ERP provides multiple advantages that help businesses operate more efficiently and stay competitive in today’s digital-first environment. Some of the key benefits include:
Cost Efficiency and Reduced IT Overhead
Cloud ERP eliminates the need for heavy upfront investments in servers, infrastructure, and in-house IT maintenance. Businesses can adopt a subscription-based model and reduce overall operational costs while accessing advanced ERP functionalities.
Scalability to Match Business Growth
As businesses grow, Cloud ERP can easily scale to accommodate more users, functions, or geographic expansion without major system overhauls. This ensures continuous operations and flexibility for future growth.
Improved Collaboration and Remote Accessibility
Being cloud-based, ERP platforms allow multi-device access from anywhere. Teams across departments or locations can collaborate seamlessly with shared dashboards and workflows, supporting remote work environments.
Streamlined Business Processes
By automating routine and repetitive tasks such as payroll, invoicing, or reporting, Cloud ERP minimizes human errors and saves time. Standardized workflows improve process efficiency and reduce operational bottlenecks.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Cloud ERP integrates customer data with sales, marketing, and service functions, helping businesses personalize interactions and respond faster to customer needs. This leads to stronger customer relationships and satisfaction.
Global Business Support
Cloud ERP supports multiple currencies, languages, and tax structures, making it easier for businesses to manage international operations without additional system modifications.
Business Intelligence
Modern Cloud ERP solutions come with built-in analytics, artificial intelligence, and reporting tools. Businesses can gain actionable insights, track performance metrics, and identify growth opportunities more effectively.
Data Security and Compliance
Cloud ERP providers ensure strong data protection through encryption, role-based access, and adherence to global compliance standards. This helps safeguard sensitive information and ensures regulatory compliance.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Cloud ERP includes backup, disaster recovery, and high-availability systems that ensure minimal disruption in case of failures or security incidents. This ensures uninterrupted business operations.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Vendors manage system updates, patches, and upgrades automatically. Businesses always use the latest version of the ERP software without having to schedule downtime or invest in additional IT resources.
Customization and Flexibility
Cloud ERP systems can be customized with industry-specific modules and workflows. Businesses can adapt the platform to their operational requirements and modify it as their needs evolve.
Competitive Advantage for Startups and SMEs
By making enterprise-level solutions more affordable, Cloud ERP helps small and mid-sized companies access tools that were previously limited to large enterprises. This levels the playing field and allows them to compete more effectively.
For startups and mid-sized businesses, these benefits level the playing field against larger competitors.
Cloud ERP Concepts
To fully understand the value of Cloud ERP, it’s important to explore some of the fundamental concepts that define how these systems work and why they are so effective for modern businesses.
Multi-Tenancy
Cloud ERP solutions are often built on a multi-tenant architecture. This means that multiple customers or organizations share the same software application and infrastructure, but their data is kept completely separate and secure. Multi-tenancy allows software providers to deliver updates, enhancements, and security patches seamlessly to all users while reducing costs. For businesses, it ensures lower expenses, faster access to innovations, and a system that is always up-to-date without requiring manual intervention.
True Cloud ERP
Not all ERP systems that claim to be cloud-based are designed the same way. A true Cloud ERP is built for the cloud environment from the ground up, rather than being a traditional on-premise ERP system that has been modified to run on cloud servers. True cloud systems leverage the flexibility, scalability, and efficiency of cloud computing, enabling faster deployments, easier upgrades, and better long-term performance. This design ensures that the ERP system is optimized for today’s digital business needs.
Integration Ready
Modern businesses rely on a variety of software tools, including CRM systems, e-commerce platforms, business intelligence applications, and industry-specific solutions. Cloud ERP platforms are built to be integration-ready, meaning they can easily connect with these external systems through APIs or built-in connectors. This capability ensures smooth data flow between different business applications, eliminates data silos, and improves overall efficiency by providing a unified view of business operations.
Subscription-Based Licensing
Unlike traditional ERP systems that often require a significant upfront investment in licenses, hardware, and IT resources, Cloud ERP uses a subscription-based licensing model. Businesses typically pay on a per-user or per-module basis, which makes ERP more affordable, flexible, and predictable. This pay-as-you-go approach allows companies to scale their ERP usage based on their growth, avoid unnecessary expenses, and better manage their IT budgets.
These concepts form the foundation of modern ERP strategy.
On-Premises ERP vs. Cloud ERP: Key Difference
One of the most common dilemmas organizations face today is deciding between traditional on-premises ERP and a modern cloud ERP solution. Both approaches aim to streamline operations and centralize business processes, but the way they’re deployed and maintained makes a big difference in cost, flexibility, and long-term scalability.
| Aspect | On-Premises ERP | Cloud ERP |
| Deployment | Installed on company-owned servers and managed internally | Hosted on the vendor’s servers, accessed via the internet |
| Upfront Costs | High (hardware, licenses, IT infrastructure) | Low (subscription-based, pay-as-you-go) |
| Maintenance | Requires an in-house IT team for updates, patches, and troubleshooting | Vendor handles updates, patches, and infrastructure |
| Scalability | Limited requires costly hardware upgrades | Highly scalable-add users or modules instantly |
| Accessibility | Restricted to on-site or VPN connections | Accessible from anywhere, on any device with internet access |
| Implementation Time | Longer (months to years) | Faster (weeks to months) |
| Security & Compliance | The company controls security protocols but bears full responsibility | Vendor provides enterprise-grade encryption, compliance, and monitoring |
| Customization | High level of customization is possible, but expensive and time-consuming | Configurable, but may be less customizable than on-prem solutions |
| Ongoing Costs | High (maintenance, upgrades, IT salaries, hardware replacements) | Predictable (monthly/annual subscription fees) |
| Best For | Large enterprises with strict control, regulatory needs, and big IT budgets | Startups, SMBs, and mid-market companies need flexibility and cost savings |
ERP vs. Cloud ERP: Key Difference
The term ERP simply means enterprise resource planning-whether in the cloud or not. The key difference is where it’s hosted.
| Aspect | Traditional ERP (On-Premises) | Cloud ERP |
| Hosting | Installed on the company’s local servers and data centers | Hosted on the vendor’s cloud infrastructure, accessed via the internet |
| Cost Structure | High upfront investment (hardware, licenses, IT staff) | Subscription-based pricing (monthly/annual), lower upfront costs |
| Maintenance | Managed internally by the company’s IT team | Managed entirely by the ERP vendor |
| Accessibility | Limited to on-site access or VPN connections | Accessible anywhere, anytime, on any device with internet access |
| Updates & Upgrades | Manual upgrades, often costly and disruptive | Automatic updates included in subscription |
| Scalability | Requires additional servers and infrastructure to scale | Instantly scalable by adding users or modules |
| Implementation Time | Longer-can take months or years | Faster-often weeks to a few months |
| Security | The company is responsible for security protocols and compliance | Vendor provides enterprise-level security, encryption, and compliance support |
| Customization | Highly customizable but resource-intensive | Flexible and configurable, though sometimes less customizable |
| Best Fit | Enterprises with strict data control, compliance-heavy industries | Startups, SMBs, and mid-market businesses seeking agility and cost efficiency |
The shift from ERP to cloud ERP is much like moving from floppy disks to Google Drive-it’s faster, more collaborative, and far easier to manage.
Types of Cloud ERP Software
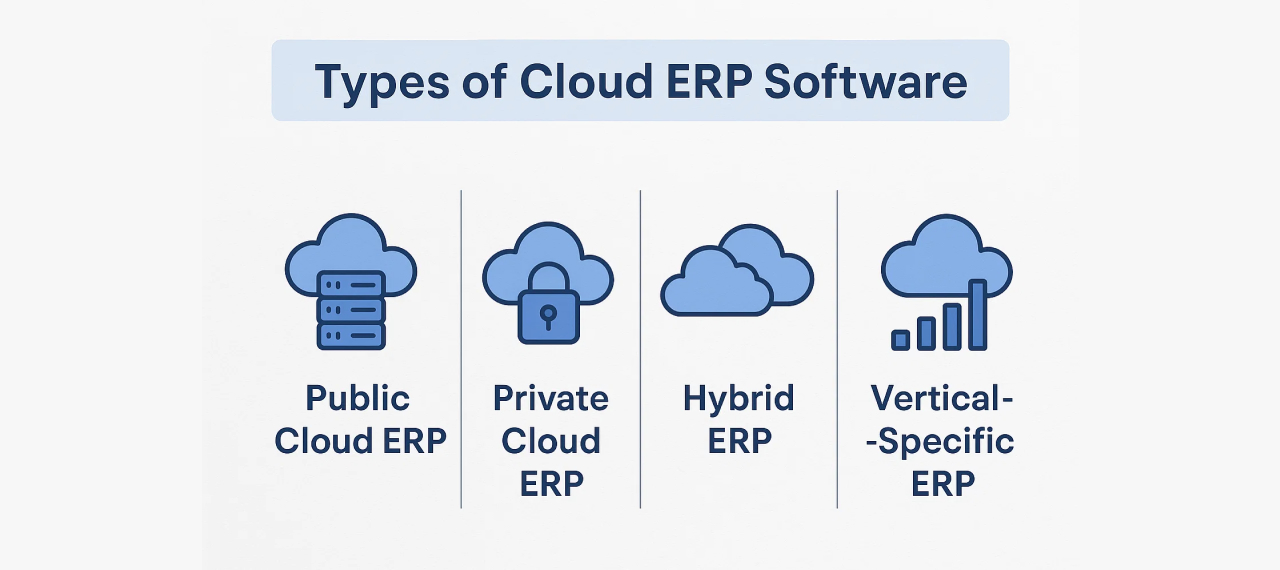
Not every business has the same operational needs, budget, or compliance requirements. That’s why cloud ERP software comes in several different types, each offering unique advantages. Understanding these options helps you choose the system that aligns with your company’s size, industry, and growth plans. For example, Cloud ERP for manufacturing focuses on production planning, supply chain optimization, and real-time analytics. Here are the main types:
1. Public Cloud ERP
Public cloud ERP solutions are hosted on shared infrastructure, meaning multiple businesses use the same software instance provided by the vendor. Data for each company is securely separated, but resources like servers and storage are shared.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective, since expenses are spread across multiple users
- Faster deployment with ready-to-use features
- Automatic updates managed by the provider
Public Cloud ERP is the best for small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) or startups that want affordability, easy scalability, and minimal IT responsibilities.
2. Private Cloud ERP
Private cloud ERP operates on infrastructure dedicated to a single organization. Unlike the public cloud, resources aren’t shared with other companies, which often means greater control, security, and customization.
Advantages:
- Enhanced security and compliance features
- More room for system customization
- Performance is not affected by other tenants
Private Cloud ERP is the best for large enterprises or businesses in highly regulated industries (like finance, defense, or healthcare) that require strict data governance and advanced control.
3. Hybrid ERP
Hybrid ERP combines both cloud and on-premises elements. Businesses may keep certain sensitive or legacy systems in-house while moving other modules-like HR, CRM, or analytics-into the cloud. This approach allows a gradual transition instead of a full migration.
Advantages:
- Flexibility to move at your own pace
- Allows companies to retain legacy investments
- Reduces risk when shifting from on-premises to cloud
Hybrid ERP is the best for organizations with complex IT environments or those hesitant to move everything to the cloud in one go.
4. Vertical-Specific ERP
Vertical-specific ERP solutions are tailored for particular industries, offering built-in modules and workflows designed around sector needs. For example:
- Manufacturing ERP – Focuses on production planning, supply chain, and quality control.
- Retail ERP – Optimized for inventory management, POS systems, and customer engagement.
- Healthcare ERP – Includes compliance features for patient data and medical supply chains.
Advantages:
- Industry-specific features without heavy customization
- Faster adoption with pre-configured tools for your sector
- Better ROI since it solves niche challenges directly
Vertical-Specific ERP is the best for Businesses in industries with unique operational requirements that generic ERP systems can’t fully address.
Your choice depends on your company’s size, budget, and compliance requirements.
Cloud ERP Challenges and Risks
Despite its advantages, cloud ERP isn’t without hurdles:
Data Migration
Migrating years of historical and transactional data from legacy systems to a new cloud ERP can be complex and time-consuming. Businesses must ensure:
- Data accuracy and consistency during transfer
- Cleaning up outdated or duplicate records before migration
- Proper mapping of fields from old systems to new ERP modules
Integration Issues
Many companies still rely on existing legacy applications for payroll, CRM, or supply chain. Integrating these with a new cloud ERP system isn’t always seamless. Challenges may include:
- Compatibility gaps between old and new software
- The need for APIs or middleware to ensure smooth data flow
- Extra costs for custom integrations
Internet Dependency
Unlike on-premises ERP, cloud ERP solutions rely heavily on stable internet connectivity. Any downtime or poor connection can disrupt:
- Real-time access to dashboards and reports
- Cloud-based collaboration across teams
- Customer service or sales operations tied to the ERP
Vendor Lock-In
Switching from one ERP provider to another is not always easy. Once a business commits to a vendor’s ecosystem, challenges can include:
- High switching costs due to data export limitations
- Re-training employees on a new system
- Risks of losing customized features
Training and Change Management
Even the most advanced ERP software won’t deliver results if employees struggle to use it. Challenges include:
- A steep learning curve for non-technical staff
- Resistance to adopting new processes
- Time and resources required for effective training
Why Mid-Market Companies Choose Cloud ERP?
Mid-market companies often operate in a unique position: they face the complexity of large enterprises but usually don’t have the same level of resources or IT budgets. This makes traditional on-premises ERP systems expensive and hard to maintain.
Cloud ERP has emerged as a game-changer for this segment because it provides:
- Lower IT Costs – No need to invest in expensive servers or hire large IT teams. Cloud ERP providers handle hosting, updates, and security.
- Flexible Pricing Models – Instead of large upfront investments, businesses can pay monthly or annually, making costs predictable and scalable as the company grows.
- Enterprise-Grade Features at Scale – Cloud ERP offers advanced capabilities (like supply chain visibility, advanced analytics, and CRM integration) that were once affordable only for large enterprises.
- Faster Global Expansion – With built-in multi-language and multi-currency support, mid-market companies can expand into international markets without adding separate ERP systems.
- Agility and Innovation – Cloud ERP updates automatically, meaning companies can quickly adopt new features and stay competitive without major system overhauls.
Market Trends and Future of Cloud ERP
The cloud ERP market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovation and the growing need for flexible, scalable business systems. Analysts estimate that by 2030, cloud ERP will dominate the ERP landscape, leaving traditional on-premises systems behind. Let’s explore the trends shaping this growth:
AI Integration in Cloud ERP
AI-powered ERP systems enable predictive analytics, process automation, and smarter decision-making, helping businesses stay ahead of demand and reduce risks.
Mobile-First ERP Design
Modern cloud ERP solutions focus on mobile accessibility, allowing employees to manage approvals, reports, and workflows directly from smartphones and tablets.
IoT Connectivity in ERP
By linking with IoT devices, ERP systems can monitor production, track assets in real time, and improve logistics efficiency, especially in manufacturing and supply chains.
Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
Vendors are moving away from generic platforms and offering ERP systems tailored to industries like retail, healthcare, and construction, ensuring a better fit and value.
Growing SME Adoption
Affordable and scalable pricing models are driving small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) to adopt cloud ERP, giving them access to enterprise-level capabilities without heavy investments.
These cloud ERP trends are shaping the global market and making it easier for companies to adopt the best cloud ERP for small businesses and mid-market firms alike.
Top Cloud ERP Providers in 2025
Top Cloud ERP Leaders like Oracle Cloud ERP or Oracle ERP Cloud remain strong contenders, while solutions like NetSuite, Acumatica, and Odoo are often considered the best cloud ERP for small businesses due to affordability and scalability.
The cloud ERP software market in 2025 is highly competitive, with several vendors offering specialized solutions for different business needs. Here are some of the leading providers to consider:
| Provider | Best For | Key Strengths |
| SAP S/4HANA Cloud | Large enterprises | Advanced analytics, scalability, global compliance, strong finance & operations |
| Oracle NetSuite | Small & mid-sized businesses (SMBs) | All-in-one ERP, financials, CRM, e-commerce, cloud-first deployment |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Businesses needing ERP + CRM integration | Seamless Microsoft ecosystem integration, CRM + ERP in one platform |
| Infor CloudSuite | Manufacturing, distribution, healthcare | Industry-specific solutions, strong supply chain, and operations support |
| Workday | HR and finance-focused companies | Workforce planning, payroll, talent management, HR-driven ERP functions |
| Acumatica | Mid-market & growing companies | Flexible pricing, modular ERP, scalability, ease of use |
| Odoo | Startups & SMEs | Open-source, affordable, customizable modules across business functions |
Each ERP provider has unique strengths. The best choice depends on your business size, industry requirements, and long-term goals.
Conclusion
Cloud ERP is more than just software-it’s a business enabler. By unifying data, streamlining operations, and enabling remote accessibility, it transforms how companies work. With advancements in AI, IoT, and industry-specific solutions, the future of ERP is firmly in the cloud. For businesses evaluating ERP solutions, the key is to map out your current challenges and growth plans, then choose a provider that aligns with your goals. Done right, cloud ERP software can be the foundation of long-term success. Working with real-time data and built-in disaster recovery. It also provides automatic updates, flexibility, and global business support.