Table of Contents
- Understanding DevSecOps
- Motivations for Transitioning to DevSecOps
- Key Principles of DevSecOps
- Implementation DevSecOps
- Challenges in Transitioning to DevSecOps
- Summarising
In today’s fast-paced technology landscape, where security threats are ever-evolving and data breaches are a constant concern, the integration of security into the development process is no longer optional; but it’s imperative now. Enter DevSecOps, a transformative approach that seamlessly incorporates security practices into DevOps processes.
In this extensive blog post, we will explore the transition from DevOps to DevSecOps, examining the motivations, key principles, best practices, and challenges involved in implementing DevSecOps within your organization.
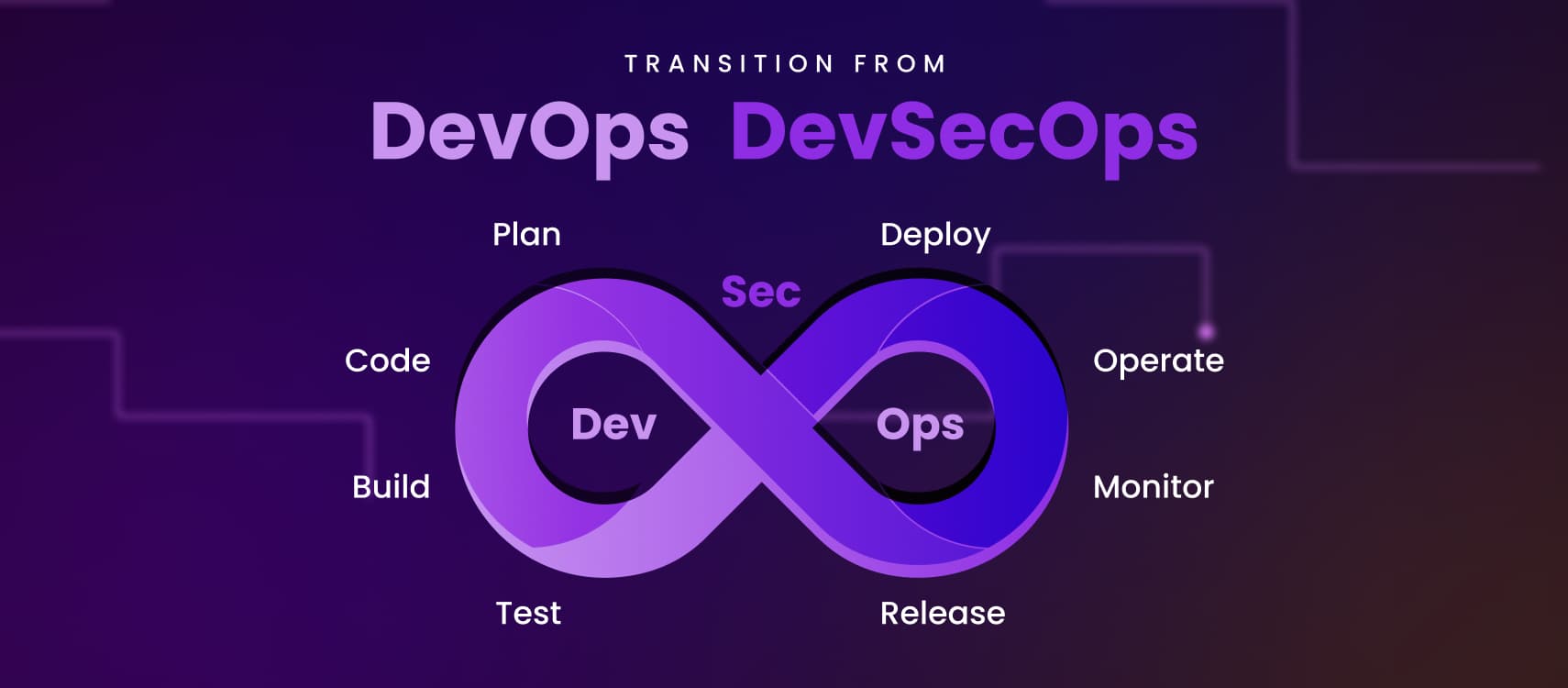
Understanding DevSecOps
DevSecOps, a fusion of Development (Dev), Security (Sec), and Operations (Ops), represents a cultural shift in how software is developed and delivered. It acknowledges that security should not be an afterthought or a separate process, but an integral part of the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC).
Traditionally, security was often seen as a bottleneck in the development process, slowing down the release cycle. DevSecOps aims to change this perception by integrating security practices seamlessly into the DevOps pipeline. It emphasizes collaboration between development, operations, and security teams, fostering a shared responsibility for security throughout the development lifecycle.
Motivations for Transitioning to DevSecOps
Several compelling reasons drive organizations to transition from DevOps to DevSecOps.
Rising Security Concerns:
The threat landscape is becoming more sophisticated, with cyberattacks and data breaches on the rise. Organizations must prioritize security to protect their data, systems, and reputation.
Regulatory Compliance:
Many industries are subject to stringent data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. DevSecOps helps organizations comply with these regulations by embedding security into their processes.
Faster Response to Threats:
DevSecOps allows for faster detection and response to security threats. By automating security testing and monitoring, organizations can mitigate risks more effectively.
Cost-Efficiency:
Addressing security issues early in the development process is more cost-effective than fixing them post-release. DevSecOps reduces the cost of addressing security vulnerabilities.
Enhanced Collaboration:
DevSecOps fosters collaboration and communication between development, operations, and security teams, breaking down silos and improving overall efficiency.
Key Principles of DevSecOps
To successfully transition to DevSecOps, organizations must embrace a set of core principles such as the ones mentioned below.
Shift-Left Security:
In DevSecOps, security is pushed “left” into the early stages of the SDLC. This means addressing security concerns from the very beginning of the development process, including during design and coding.
Automation:
Automation is a cornerstone of DevSecOps. Automated security tests, vulnerability scanning, and compliance checks ensure that security is consistently applied and that vulnerabilities are detected early.
Continuous Monitoring:
DevSecOps involves continuous monitoring of applications and systems in production. This real-time monitoring allows organizations to detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
Shared Responsibility:
Security is not the sole responsibility of the security team. All stakeholders, including developers and operations staff, share responsibility for security.
Immutable Infrastructure:
DevSecOps promotes the use of immutable infrastructure, where systems are rebuilt from scratch rather than patched. This minimizes the risk of hidden vulnerabilities.
Implementing DevSecOps: Best Practices
Transitioning to DevSecOps requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to guide your implementation:
Security Training:
Invest in training and awareness programs to educate development and operations teams about security best practices and threats.
Security Champions:
Appoint security champions within development teams who can act as advocates for security and help bridge the gap between security and development.
Automate Security Testing:
Integrate automated security testing tools into your CI/CD pipeline to scan code for vulnerabilities, identify misconfigurations, and assess compliance.
Code Review:
Implement code review processes that include security-focused reviews to identify and address security issues early.
Threat Modeling:
Incorporate threat modeling into the design phase to identify potential security risks and devise strategies to mitigate them.
Container Security:
If using containers, ensure container images are scanned for vulnerabilities before deployment. Container security tools can automate this process.
API Security:
Pay attention to API security, as APIs are often targeted by attackers. Implement strong authentication, access controls, and encryption for APIs.
Logging and Monitoring:
Set up comprehensive logging and monitoring solutions to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time.
Incident Response Plan:
Develop an incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a security breach. Test and refine the plan regularly.
Compliance as Code:
Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and Compliance as Code (CaC) to define and enforce security policies for your infrastructure and applications.
Challenges in Transitioning to DevSecOps
While the benefits of DevSecOps are significant, organizations may encounter challenges during the transition. Here we mention a few of them.
Cultural Resistance:
Shifting to a DevSecOps culture can be met with resistance, especially if security was previously considered a separate function.
Tooling Complexity:
Integrating security tools into the CI/CD pipeline can be complex. Selecting the right tools and ensuring they work seamlessly can be challenging.
Skills Gap:
Organizations may lack the necessary security expertise to implement DevSecOps effectively. Training and upskilling are essential.
Legacy Systems:
Legacy applications and systems may pose challenges in implementing DevSecOps practices, as they may not designed with security in mind.
Compliance Requirements:
Meeting compliance requirements, especially in highly regulated industries, can be demanding. DevSecOps practices must align with regulatory standards.
Summarising
The transition from DevOps to DevSecOps is not just a technical shift; it represents a fundamental change in how organizations approach security in software development. By embedding security practices into every stage of the development lifecycle, organizations can proactively address security threats, comply with regulations, and enhance their overall security posture.
While the journey to DevSecOps may involve challenges, the benefits such as improved security, faster response to threats, and a culture of shared responsibility, make it a worthy endeavour. As the technology landscape continues to evolve, DevSecOps will remain a critical approach to safeguarding digital assets and ensuring the resilience of modern organizations.