Table of Contents
- What is a Full-Stack Developer?
- The Advantages of Hiring Full-Stack Developers
- Leading Tech Stacks in the Full-Stack Development Landscape
- The Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Full Stack Development
- Conclusion
The pace of technological advancement has reached unprecedented levels. The software development process transforms new frameworks and cloud platforms, and AI-powered tools. The full-stack developer position maintains its position as a fundamental role despite all technological advancements.
Modern businesses require complete digital solutions that deliver fast performance and scalability and provide excellent user experiences. A person who masters both front-end user experience and back-end system operation is the perfect candidate to create complete digital solutions.
The actual question focuses on how full-stack development will evolve in the upcoming years. The role of full-stack development will transform through the integration of AI systems, low-code platforms, and cloud-native technologies. Will specialization replace the current practice of full-stack development?
This article examines the current trends affecting full-stack development while explaining its benefits for developers and businesses and explaining why this skill set will stay essential through the next decade.
The following article provides information about industry trends, full-stack developer evolution, and success strategies for the future.
What is a Full-Stack Developer?
Organizations operating in a digital-first environment must decide between employing front-end developers and back-end developers, or sometimes both developers, for their projects. The management of multiple specialists for projects leads to increased complexity and higher costs. Businesses frequently choose full-stack developers as their solution. These developers possess all the necessary skills to handle complete development requirements from start to finish.
Full-stack developers possess expertise in both front-end development, which handles user interface elements, and back-end development, which handles server operations, database management, and all hidden system processes. Full-stack developers possess the ability to create complete applications from start to finish because they understand both front-end and back-end development without requiring ongoing support from different teams.
Understanding the Role of a Full-Stack Developer
Full-stack developers prove their versatility by wearing multiple roles at once because they excel at both UI design and server programming and live system deployment. The developer handles both front-end user interface development and back-end server operations and deployment tasks with equal proficiency. The developer creates user-friendly interfaces with interactive elements through responsive design while handling database operations, secure request processing, and data management.
The developer’s skills reach beyond integration and deployment work. The developer knows how different application layers function together, and they use this knowledge to deploy solutions that reduce system downtime during production deployment. A full-stack developer uses their wide range of skills to monitor the complete system structure of projects instead of performing individual tasks.
Front-End Expertise
The front-end serves as the first point of contact for users, and full-stack developers deliver their most significant value in this area. Full-stack developers utilize HTML, CSS, and JavaScript fundamentals to create interactive web interfaces through modern frameworks, including React, Angular, and Vue.js. The developer must achieve both visual attractiveness and user-friendly functionality for applications that operate across multiple devices and browser platforms.
A full-stack developer creates user-friendly interfaces for customer portals through their work, which includes smooth interactions and mobile-desktop screen compatibility, and a consistent user experience. Their unique blend of technical skills and design understanding enables them to build interfaces that deliver high user satisfaction.
Back-End Knowledge
The front-end section of an application draws user interest, but the back-end operates as the core system that sustains application functionality. Full-stack developers possess equal mastery of both front-end and back-end development domains. Full-stack developers create server-side code using programming languages including Java and Python, PHP and Ruby, and Node.js. The developer’s expertise includes building APIs and database connections and implementing authentication systems with security protocols.
The developer’s work involves making sure button clicks result in fast request processing, which produces accurate responses. The developer creates data management systems that protect information while optimizing system speed and enabling the application to expand its capacity. The result for businesses becomes a visually appealing product that operates dependably from the inside out.
Database Management Skills
Full-stack developers demonstrate their expertise through their ability to handle database management tasks. Applications need efficient database structures to succeed because they depend on data storage, yet poor database management can cause otherwise excellent applications to fail. Full-stack developers possess expertise in database management through their ability to work with relational databases, MySQL and PostgreSQL, and NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB and Cassandra.
The developers establish product catalogs for e-commerce sites and customer record management systems in CRM applications while maintaining data accuracy, security, and accessibility. The developers optimize database queries to achieve fast application performance because this directly affects user satisfaction and system performance.
API Development and Integration
Modern applications function independently of other systems. The integration of applications with external services, including payment processors and mapping tools, social media platforms, and third-party applications, requires APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). Full-stack developers possess expertise in developing APIs and implementing existing ones.
A full-stack developer can integrate payment gateways into business applications through seamless implementation, which provides customers with secure transaction processing. The full-stack developer’s expertise in integration management enables applications to function as part of a unified digital network.
DevOps and Deployment Knowledge
Full-stack developers continue their work after finishing the coding process. The deployment process and fundamental DevOps practices are part of their expertise, which enables them to transfer applications between development and production environments. Full-stack developers work with cloud platforms AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud and demonstrate proficiency in Docker and Kubernetes tools.
The process of application deployment requires more than simple live deployment because it needs server setup and performance monitoring, scalability management, and workflow automation. Full-stack developers provide essential expertise that enables them to deploy projects from development to successful launch and ongoing maintenance.
Problem-Solving and End-to-End Vision
A full-stack developer’s greatest strength comes from their ability to understand the complete system architecture. Their knowledge of all development layers enables them to recognize connections that specialists might miss. A full-stack developer can track down front-end bugs to their source in the back-end system or database. The developer can determine the source of application slowness by examining code quality and server performance, and database query efficiency.
Their ability to view the entire system enables them to solve problems efficiently. The developer handles both short-term problems and plans for future development while ensuring system scalability and performance. The business advantages of this complete system understanding are that it results in applications that are both robust and dependable.
The Advantages of Hiring Full-Stack Developers
Businesses operating in today’s digital environment require developers who handle diverse project demands while maintaining project deadlines. Full-stack developers excel in this situation because they possess the ability to handle all aspects of development. Hire Full-stack developers who possess a complete set of skills that enable them to handle the entire project lifecycle from initial concept development through design work and coding, testing, and deployment stages.
Here are the key advantages of hiring full-stack developers:
Versatility and Flexibility
Full-stack developers excel because they possess the capability to work throughout the complete technology stack. The developers possess expertise in both front-end development tools (React, Angular, Vue.js) and back-end development frameworks (Node.js, Django, Spring Boot). The developers possess the ability to move between user interface development and database administration tasks with ease.
- Switch seamlessly between designing user interfaces and managing databases.
- Adapt quickly to changing project requirements.
- Provide end-to-end solutions without relying heavily on multiple specialists.
For businesses, this flexibility means fewer bottlenecks and smoother progress, especially in projects that require constant iteration and innovation.
Cost-Effectiveness
The process of hiring individual developers for front-end work, back-end work, database administration, and testing functions leads to substantial project expenses. A full-stack developer eliminates the requirement for multiple specialists because they can perform all necessary tasks independently.
The hiring process becomes more efficient because it eliminates the need for extensive team coordination. The employment of one proficient developer who handles various tasks enables startups and small to medium businesses to optimize their resources effectively while delivering high-quality results.
Streamlined Communication
Large teams experience regular communication breakdowns. The lack of understanding between front-end and back-end developers results in project delays, requires additional work, and produces different results. A full-stack developer connects the development process because they possess knowledge of both front-end and back-end operations.
With a single point of contact, businesses can:
- Simplified project dialogue becomes possible.
- The teams experience fewer instances of confusion.
- Ensure consistency in coding standards and design approaches.
The improved communication process enables better team collaboration, which results in faster project advancement.
Faster Development Time
The current market demands fast delivery because speed represents a critical factor for success. Full-stack developers speed up development time because they work on different project layers at the same time. The developer can establish back-end APIs while simultaneously creating front-end components to achieve seamless integration.
Their project understanding enables them to perform multiple tasks at once, which decreases their need for other team members to complete their work, thus delivering projects faster. The quick development time enables businesses to introduce their products early, which helps them establish market leadership.
Comprehensive Problem-Solving
The solution of complex technical problems requires examination of all application layers. A front-end bug that appears to users actually stems from problems located in the back-end system or database. A full-stack developer possesses the necessary broad understanding to effectively track down and solve complex problems throughout the system.
Their cross-disciplinary knowledge allows them to:
- Identify the root cause of problems.
- The developer provides complete system-focused solutions that surpass individual component solutions.
- The developer optimizes operational processes to stop future problems from occurring.
Their ability to solve problems in a complete manner makes them essential for creating software systems that are both strong, expandable, and dependable.
Better and Faster Troubleshooting
When something goes wrong, businesses can’t afford long delays. Full-stack developers bring speed and precision to troubleshooting because they know the system end-to-end. They can test, debug, and fix errors across the front-end, back-end, and database without needing to involve multiple specialists.
This reduces downtime, ensures faster recovery, and keeps projects running smoothly. Their troubleshooting skills are especially critical in live environments where quick fixes can prevent customer dissatisfaction or revenue loss.
Quality Enhancement
Quality in software development requires more than clean code because it must deliver an uninterrupted user experience. Full-stack developers guarantee that the front-end user experience matches perfectly with the back-end operational performance. The developers who handle projects from start to finish preserve design consistency and maintain logical and functional coherence between all elements.
They also bring a unique perspective: since they oversee the project from start to finish, they can identify improvement areas at every stage. This results in higher-quality applications with fewer errors, stronger performance, and better scalability.
Leading Tech Stacks in the Full-Stack Development Landscape
Software development businesses seek solutions to create applications that deliver fast performance alongside scalability and user-friendly interfaces in today’s rapidly changing technology environment. The most effective method to reach this goal involves using full-stack development frameworks together with appropriate tools.
Full-stack developers handle front-end user interface development, back-end server operations and database management, and API development. Developers select specific tech stacks that combine programming languages, frameworks, and tools to optimize their work process and enhance their productivity when working on both front-end and back-end development.
The numerous available options make it difficult to identify which stacks provide the most value. This article examines the dominant tech stacks that control full-stack development while discussing their benefits and drawbacks and business adoption patterns.
1. MEAN Stack
Components: MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js
The MEAN stack represents a widely used JavaScript framework within the JavaScript ecosystem. The MEAN stack enables developers to work with a single programming language because it unites front-end and back-end technologies that share JavaScript as their common language.
Why MEAN Is Popular
- Single Language Development: Everything runs on JavaScript, reducing the need to switch contexts.
- Angular Power: Angular enables building dynamic single-page applications (SPAs) with rich user experiences.
- Node.js Scalability: High-performance back-end, capable of handling large-scale traffic.
Pros
- Unified development language.
- Strong support community.
- Ideal for SPAs and cloud-based apps.
Cons
- Angular has a steeper learning curve than React.
- Not always the best for heavy CPU-bound apps.
Best Use Cases
- Enterprise web applications.
- Real-time chat apps or collaboration tools.
- Cloud-native apps require scalability.
2. MERN Stack
Components: MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js
The MERN stack operates similarly to MEAN because it uses React instead of Angular as its front-end library, which belongs to Facebook. The MERN stack has gained immense popularity because React provides lightweight functionality and flexibility, and receives support from a massive developer community.
Why MERN Is Popular
- Reusable Components: React’s modular nature speeds up UI development.
- Virtual DOM: Faster rendering and performance improvements.
- Strong Ecosystem: Supported by Facebook and widely used in startups and enterprises alike.
Pros
- Rapid UI development with React.
- Wide talent pool for hiring.
- Excellent for highly interactive applications.
Cons
- React is a library, not a full-fledged framework (requires third-party tools).
- Handling SEO can be tricky without server-side rendering (SSR).
Best Use Cases
3. Django (Python-Based)
Framework: Django (with Python, SQL/NoSQL databases)
The Python framework Django provides developers with high-level functionality that delivers fast performance while maintaining strong security features and flexible scalability. The framework uses Model-View-Template (MVT) architecture and includes numerous built-in features that help developers work more efficiently.
Why Django Is Popular
- “Batteries-Included” Philosophy: Includes admin panels, authentication, and security tools by default.
- AI/ML Ready: Since it’s Python-based, Django integrates easily with AI/ML libraries.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Prevents SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and other common attacks.
Pros
- Strong for data-heavy apps.
- Excellent documentation and community.
- Reduces boilerplate coding.
Cons
- It can be heavy for small projects.
- Less flexible than Node.js stacks.
Best Use Cases
- Fintech apps require security.
- Healthcare platforms.
- SaaS applications.
- AI-powered solutions.
4. Ruby on Rails
Framework: Ruby on Rails (with Ruby, SQL/NoSQL databases)
Ruby on Rails (RoR) provides developers with tools to create web applications at a faster pace and with greater ease of use. The framework operates based on convention over configuration, which minimizes the need for developers to write repetitive code.
Why RoR Is Popular
- Speed of Development: Great for startups needing MVPs.
- Rich Libraries (Gems): Extend functionality quickly.
- Readable Syntax: Developers love its clean, human-readable code.
Pros
Rapid prototyping.
Encourages maintainable code.
Huge ecosystem of gems.
Cons
It can be slower than Node.js for very large apps.
Smaller talent pool compared to JavaScript and Python.
Best Use Cases
- Startups building MVPs.
- E-commerce platforms.
- Content-heavy applications.
5. LAMP Stack
Components: Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Python/Perl
The LAMP stack represents one of the earliest and most dependable full-stack combinations that developers have used for many years. The LAMP stack continues to be widely used because it offers stability and broad platform support, even though newer technology stacks have emerged.
Why LAMP Is Popular
- Proven Reliability: Powers countless websites, including WordPress and Drupal.
- Open Source: Cost-effective with extensive documentation.
- Flexibility: Each component can be swapped with modern alternatives (e.g., Nginx instead of Apache).
Pros
- Cost-effective and widely supported.
- Great for traditional web hosting.
- Strong database support with MySQL.
Cons
- Less modern compared to Node.js stacks.
- Not ideal for real-time applications.
Best Use Cases
- Content management systems (WordPress, Joomla).
- Blogs, news portals, and e-learning sites.
- Small-to-medium enterprise apps.
6. Bootstrap (Front-End Framework)
Framework: Bootstrap (HTML, CSS, JavaScript Toolkit)
Bootstrap functions as a front-end tool, but it does not complete the full stack development process. The platform enables developers to create responsive interfaces through its pre-designed components and utility tools, which speed up the design process.
Why Bootstrap Is Popular
- Responsive by Default: Apps look great across devices.
- Ready-to-Use UI Components: Saves design and development time.
- Integrates with Any Stack: Works seamlessly with MEAN, MERN, Django, and more.
Pros
- Faster front-end development.
- Huge library of templates.
- Beginner-friendly.
Cons
- It can lead to “generic” looking websites if overused.
- Limited customization without manual tweaks.
Best Use Cases
- Prototyping applications.
- Small-to-medium projects where time is critical.
- Enterprises need consistent design standards.
Comparing Tech Stacks
| Stack | Language | Strengths | Best For |
| MEAN | JavaScript | Unified language, scalability | SPAs, real-time apps |
| MERN | JavaScript | React’s flexibility, UI speed | Dashboards, eCommerce |
| Django | Python | Security, data-heavy apps | Fintech, SaaS |
| Ruby on Rails | Ruby | Rapid MVP development | Startups, eCommerce |
| LAMP | PHP/Python | Proven reliability, CMS-friendly | WordPress, enterprise sites |
| Bootstrap | CSS/JS Toolkit | Responsive design, fast UI dev | Prototypes, enterprise UI |
The Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Full Stack Development
Full-stack development continues to experience rapid transformation at an unprecedented rate. The development process for applications undergoes fundamental changes through cloud computing and microservices, containerization, and serverless architecture, which move beyond being industry trends to become actual deployment and scaling tools for developers.
Full-stack developers today avoid the need to handle physical infrastructure management because of modern technology advancements. Developers now dedicate their time to business problem-solving, user interface optimization, and high-quality code development. The following discussion examines how new technologies transform the complete development process for full-stack developers.
Cloud Computing

Cloud computing has transformed application development through its ability to deliver flexible computing resources that scale according to demand. Developers can access instant deployment of servers, databases, and storage through platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud without needing physical equipment.
This shift has several benefits for full-stack development:
- Seamless Scaling: The system automatically adjusts its capacity through server addition for horizontal scaling and resource enhancement for vertical scaling based on user demand.
- Cost Efficiency: The pay-per-use pricing model of cloud computing allows businesses to spend only on their actual resource utilization, which minimizes their initial expenses.
- Global Collaboration: Teams located in different parts of the world can use cloud-based infrastructure to work together effectively, which enhances both development and deployment operations.
Cloud computing enables developers to concentrate on feature development because it handles all infrastructure management tasks.
Microservice Architecture
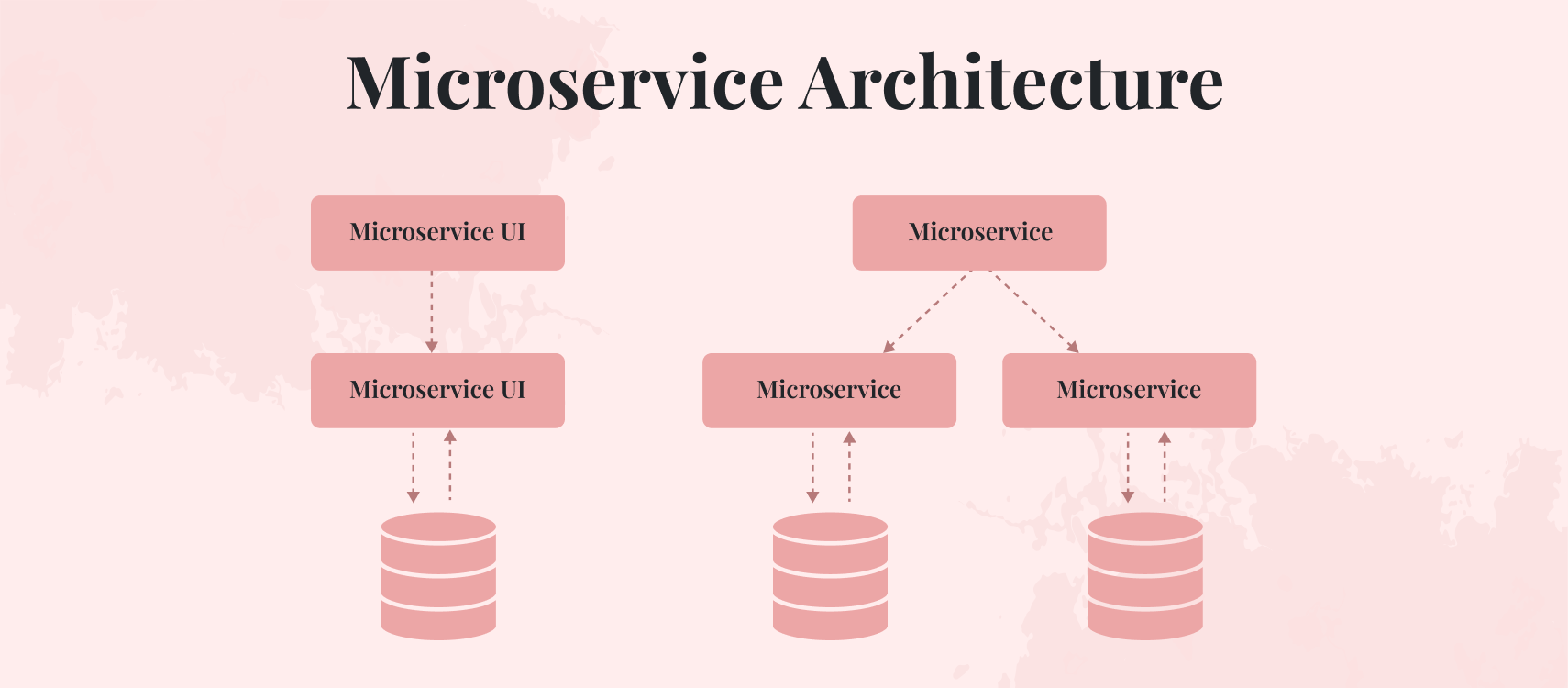
Microservices architecture is another technology that has transformed full-stack development. This approach involves breaking down monolithic applications into smaller services that can be deployed and scaled independently of each other as per specific requirements.
By leveraging this architecture. Developers can use different technologies in each microservice with ease while promoting team autonomy throughout the development cycle. Lastly, containerization technology enabled by Docker provides a consistent and isolated environment for applications, enabling consistent deployment across different environments from development to production with enhanced collaboration between development teams.
As a whole, these technological innovations continue to have a profound impact on full-stack development by allowing developers to build better solutions faster without worrying too much about infrastructure management or deployment logistics.
Serverless Architecture & Containers
The use of containers provides developers with fast scalability and efficient resource management, which allows them to control application scaling better than other methods for full-stack developers who handle resources based on demand levels.
Serverless architecture creates new possibilities for full-stack developers who can focus on code development and application logic because infrastructure management becomes abstracted from their responsibilities, which leads to improved development and deployment workflows.
Serverless systems operate with cost optimization through usage-based billing, which eliminates the need for idle resource maintenance and unused resource provisioning. Serverless platforms automatically expand their capacity to match demand changes without needing developer intervention for manual scaling adjustments.
Serverless architecture allows platform providers to handle specific operational tasks, which leads to significant reductions in total operational costs.
Conclusion
The job market for full-stack developers has reached its highest point ever. The industry transformation through new technologies has led businesses to seek professionals who can link front-end and back-end operations to create applications that deliver scalability, security, and high performance.
Full-stack developers who master containerization and AI integration skills can lead innovation because of the growing demand for cross-platform development serverless architecture and cloud computing. The ability of full-stack developers to adapt to new technologies enables organizations to create better user experiences and optimize workflows while maintaining market competitiveness in the fast-evolving digital environment.
Full-stack developers have evolved beyond their coding role to become strategic problem-solvers who enable businesses to maximize their use of new technologies.